OpenMusic Reference
x-union

x-union
(sets module) -- merges two sets
Syntax
x-union l1? l2? &optional test key &rest list
Inputs
| name | data type(s) | comments |
|---|---|---|
| l1? | a list or tree | |
| l2? | a list or tree | |
| test | a function name or lambda function | optional; the function with which to compare the two lists. Defaults to ‘equal’ |
| key | a function name or lambda function | optional; a function to apply to the lists before comparison. Defaults to ‘identity’ |
| list | list | optional, extensible; additional lists to be compared. |
Output
output| data type(s)| comments
—|—|—
first| a list| a single list, the union of l1? and l2? (and list
s, if present)
Description
Normally, this box merges two sets, l1? and l2? , into a single list, with no repetitions.*
 |
*There is an exception: x-union does not remove duplicate elements if they both occur within one of the original lists. If you need to be sure that the resulting list contains no duplicates, use remove-dup .
—|—
If the optional test argument is added, the lists can be compared according to any predicate. The default value of test is ‘equal. Only elements in the first list that return nil when compared with all the elements in the second list (according to the predicate) are returned in the result list, along with all the elements of the second list. Since the default comparison returns t if the elements are equal, elements in the first list which also occur in the second list are eliminated.
If the key argument is included (the default function is identity ), the function at key is first evaluated using each of l1? ‘s elements as input, and then the lists are compared according to the test on the results of the function. test and key may be either the name of a predicate function or a connected function or subpatch icon in lambda mode.
Additional lists can be compared by adding list inputs.
 |
When using test s other than the default, this function is not commutative
—|—
Examples
Finding the union of two sets
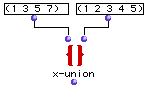
This mergers the two sets and returns: ? OM->(7 1 3 4 5)
| Prev | Home | Next |
|---|---|---|
| x-intersect | Up | x-xor |