OpenMusic Tutorials
Prev| Chapter 4. Flow Control I: Predicates| Next
Tutorial 14: Random construction of a sequence
Introduction to omif
Topics
The idea of flow control; introduction to conditional functions and predicates.
Key Modules Used
The Concept:
This patch uses the omif module to choose between two possible evaluations based on the outcome of the predicate module om= . The structure for generating the random notes is otherwise similar to the previous two tutorials’.
The Patch:
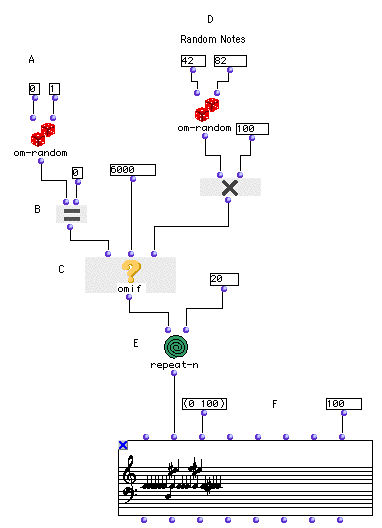
At (A), we will use om-random as a ‘coin toss’ generating 0 or 1.
om= is what is called a predicate. Predicates perform some kind of test and then return true or false. “True” in OM is represented by a special data type called the truth value, t. “False” is usually represented by the empty set, nil, although most conditional controls will take anything not t as a “false” value.
Predicates are usually used as tests which feed into other modules controlling program flow. The flow of a program or an OM patch determines what will be done and in what order. OM patches are flowcharts which graphically represent this flow. Mastering flow control is an important part of learning to program because without it patches will always act the same way.
om= (B) tests the output of om-random against its second argument, 0. If om-random outputs a zero, the test will be true and will return the truth value t. If the output of om-random is 1, om= will return nil for false.
omif is a module used to control program flow. It is modeled on the simple if - then - else syntax you may be familiar with from other programming languages. Its function can be summarized:

If it receives t at its first input, it evaluates whatever is connected to its second input. If not, it outputs nil. There is a third, optional input which can be added by selecting the function and hitting option- ->. If this third input is present, omif evaluates it instead of returning nil when the predicate at the test input is false.
So, repeat-n (E) calls omif (C) 20 times. Each time, the predicate om= is evaluated against the random result of om-random . If the test is true, omif passes 6000. If it is false, the other branch of the patch is evaluated producing a random middic between 4200 and 8200. The results are collected in a Chord-seq.
| Prev | Home | Next |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Control I: Predicates | Up | Flow Control II: Loops |