| Navigation : Previous | Next |
Lambda Mode Examples: Test Functions
Some functions have a test argument. This test argument determines the way the function operates on data. For instance, it can set comparaison rules for a sorting process, conditions to fulfill reject items from a list, etc.
This test can therefore be modified by specifying a function, or more generally a lambda function, which allows to modify the behaviour of the initial function.
Example : Removing Duplicates in a List
The remove-dup function tests if the items of a list are equal pairwise , and if so, removes duplicates from the pair.
-
Its first argument is a list.
-
Its second argument is a test function. This test function determines the nature of the “equal” test. It has a default value : ‘eql. Values are compared with the Lisp eql function.
—|—
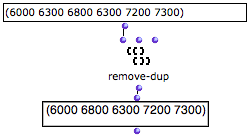
removing duplicates : One of the two occurences of 6300 has been removed from the input list.
Defining a New Test Function
We would like to remove octaves from a list of pitches, but there is no such function in OM. To do so, we can use remove-dup with a new test function that can detect octaves in the input pitch list. For instance, the previous example has two duplicates : 6000 and 7200, a C4 and a C5.
Values can be considered equal according to the octave interval, if they are compared modulo[1] the octave interval .
Note that an octave = 1200 cents.
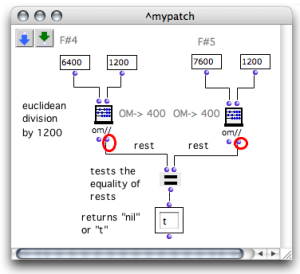
The following patch tests if the pitches are equal modulo an octave with the function om//.
-
The first output of om// returns the quotient of the division.
-
The second output returns the remainder of the division.
The = predicate tests if the remainders of the division by 1200 of two elements are equal, that is, if these two elements are equal modulo 1200.
—|—
Modulo and Octave
- Two values are “equal the same modulo” when their division by the same divisor produces the same remainder .
An octave = 1200 cents. If two values are “equal modulo 1200” they have an octave relation. This mieans that an euclidean division by 1200 should return the same remainder.
- For instance : C4 is equal to 6000, C5 to 7200. F#4 is equal to 6400, F#5 to 7600.
C4 : (6000 / 1200) = 5, remainder 0
C5 : (7200 / 1200) = 6, remainder 0
F#4 : (6400 / 1200) = 5, remainder 4
F#5 : (7600 / 1200) = 6, remainder 4
—|—
Modifying the Function Behaviour
The new test function can now become the test argument and replace the defautt eql test of remove-dup .
-
The patch, now on “lambda” mode is connected to remove-dup as a test argument.
-
The two inlets of the patch indicate that the lambda function takes two arguments.
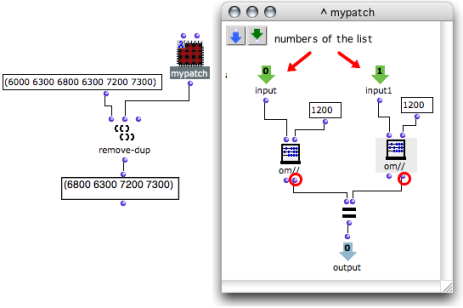
Remove-dup can now remove all values whose modulo 1200 is equal to the modulo 1200 of another value.
Lambda Patch
General Issues with Lambda Functions
References :
*[1] Modulo
In computing, the modulo operation finds the remainder of division of one number by another. If two numbers, a and b , when divided by the same n divisor , have the same remainder, they are ” equal modulo n “.
-> If remainder ( a / n ) = remainder ( b / n ), a = b , modulo n .
Contents :
- OpenMusic Documentation
- OM User Manual
- OpenMusic QuickStart
| Navigation : Previous | Next |