| Navigation : Previous | Next |
OMif : If, Then, Else
The behaviour of omif can be described by the following proposition : “IF the A condition is verified, THEN execute the B operation, ELSE execute the C operation”.
The omif box can be accessed via the Functions / Kernel / Control / OMIF menu (or typing “OMIF” in the patch window).
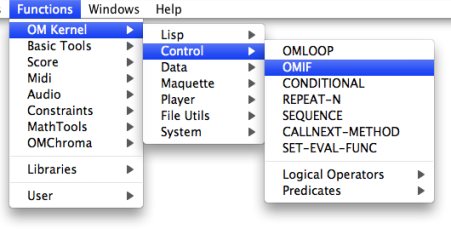
Box Inputs
Omif has two default inputs and one optional input :
- “test” stands for “if” : it represents the test of a condition in a given proposition.
- “action” stands for “then” : it represents the consequence of the test in the same proposition.
- “else” : allows to perform another operation if the condition is not fulfilled.
Each input accepts a function, a factory, or a data box.
To add or delete the optional “else” argument : press Alt +<- or -> /
SHIFT + > or <.
Behaviour
“Test” evaluates the box it is connected to and checks if a number of conditions for the operation are fulfilled.
- If the box yields something else than “nil”, the conditional test is verified, and “ then” evaluates the box connected to its second input.
- It the box yields “nil”, OMIF returns the same “nil” value.
Omif is evaluated like any other box, and returns the value yielded by “then” or “else”.
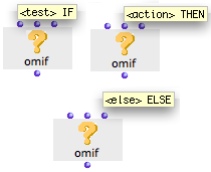
Example : IF, THEN
Here, “test” evaluates the om= predicate, which checks if the value returned by om-random is equal to 2.
- If the condition is not fulfilled, om= and OMIF return “nil”.
- If the condition is fulfilled, OMIF evaluates the data box connected to its second input, and returns “blue”.
Here, “test” is determined by the om= predicate, but it can also be connected to any other type of box.
For Full Information about Predicates :
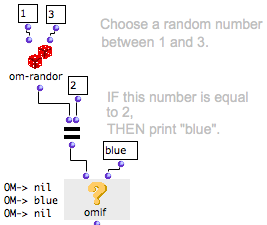
Example : IF, THEN, ELSE
In this example, “else” has been added to OMIF. If the condition is not fulfilled, OMIF doesn’t return “nil”, but the random number.
Adding Optional Arguments:
Contents :
- OpenMusic Documentation
- OM User Manual
- OpenMusic QuickStart
| Navigation : Previous | Next |