OpenMusic Reference
sum

sum
(control module) -- returns the sum of its collected elements
Syntax
sum what? &optional retard
Inputs
| name | data type(s) | comments |
|---|---|---|
| what? | a number | |
| retard | a function name or lambda function |
Output
| output | data type(s) | comments |
|---|---|---|
| first | a number | triggers the collection |
| second | a number | returns the state of the collection without evaluation |
| third | 0 | reinitializes the counter, resetting it to zero |
Description
 |
sum is part of a group of functions for performing iterative loops. They can only be used within an omloop patch window. Since they only function within the context of the entire repeating loop, they (or any function connected to them) cannot be evaluated directly within the patch window. You must evaluate the entire loop. See the entry on omloop for more information.
—|—
sum is a type of collector. It returns the sum of all the results of the loop.
Like all collectors, sum has three outputs:
The first output triggers the collector, evaluating whatever is connected to it and adding that result to the value already stored by previous repetitions of the loop. It is usually connected to eachTime . The value carried by the connection itself is the running total, which you can verify by placing the lisp function print between the first output and eachTime .
The second output returns the current state of the collector, without evaluating whatever is connected to it. It is usually connected to finally so that you can get the results of the addition.
The third output reinitializes the collector, resetting it to zero. The value carried by the connection is always 0.
Examples
 |
About the collectors |
|---|---|
sum is a type of collector. The most generalized type of collector is the function accumulator . Some collectors are special versions of the accumulator function. In these cases, the example of the use of the specific collector is reproduced with accumulator to illustrate this. The reader is therefore advised to read the entry on accumulator before continuing.
Using sum
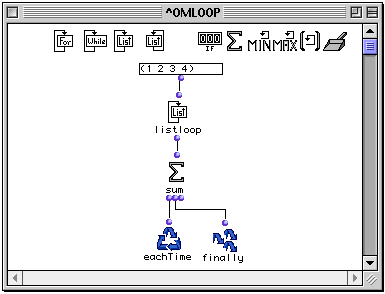
This simple example adds the elements (1 2 3 4). They are passed individually to sum , which adds each to the previous total. The output is:
? OM->10
Reproducing sum with accumulator
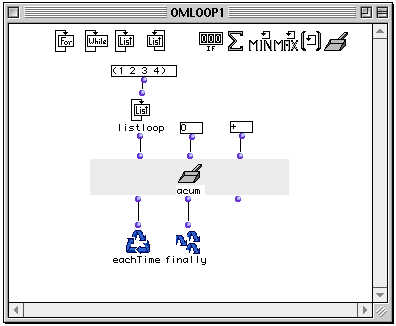
We will set up accumulator to perform exactly the same function. The listloop output of (1 2 3 4) is run into the first input. We set the initial value to zero and connect the function + to the fun input. At each iteration, the previous value of accumulator and the current value of listloop are passed to + . The result is stored, becoming the current value of accumulator for the next pass.
| Prev | Home | Next |
|---|---|---|
| counter (count) | Up | minim (min) |